Teaching Files
Archived Case 49
Contributed by: Katherine E. Dee, MD -
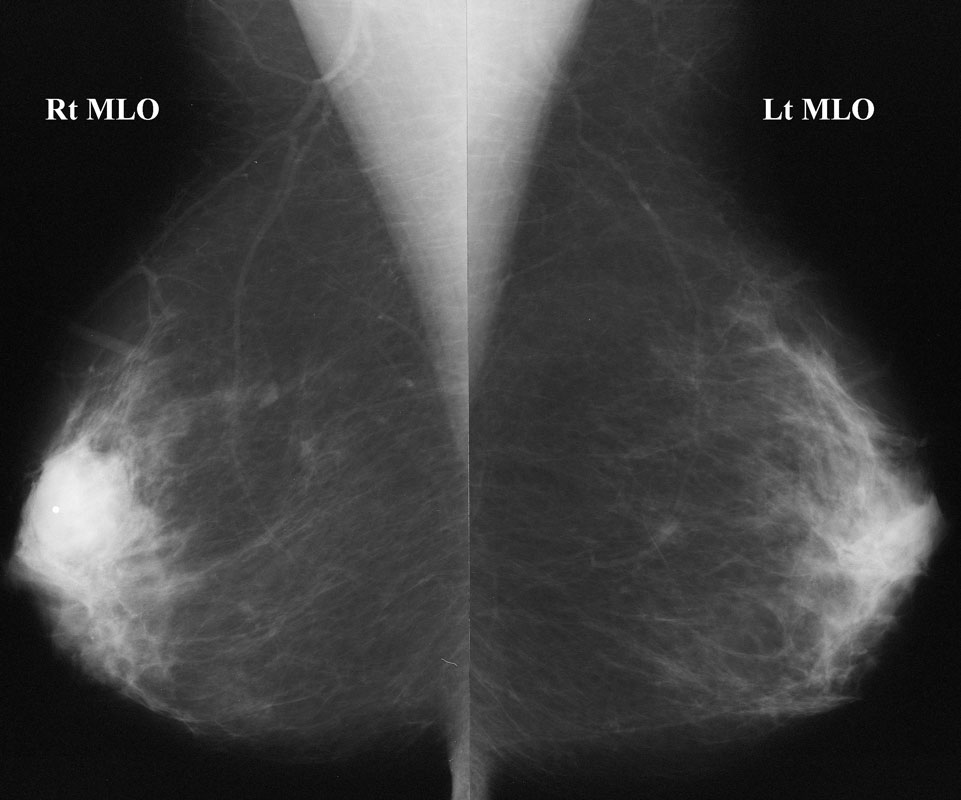
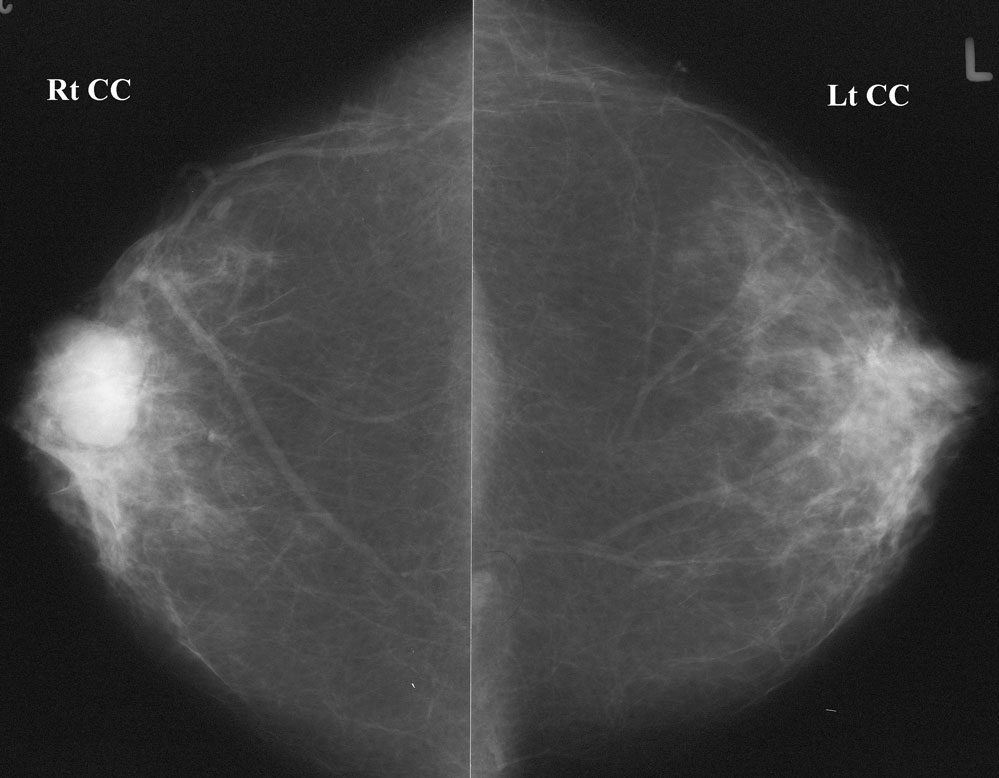
Spot compression magnification mammography
MRI
a and b
a b and c
should be performed for palpable findings unless the area is entirely fat on the mammogram.
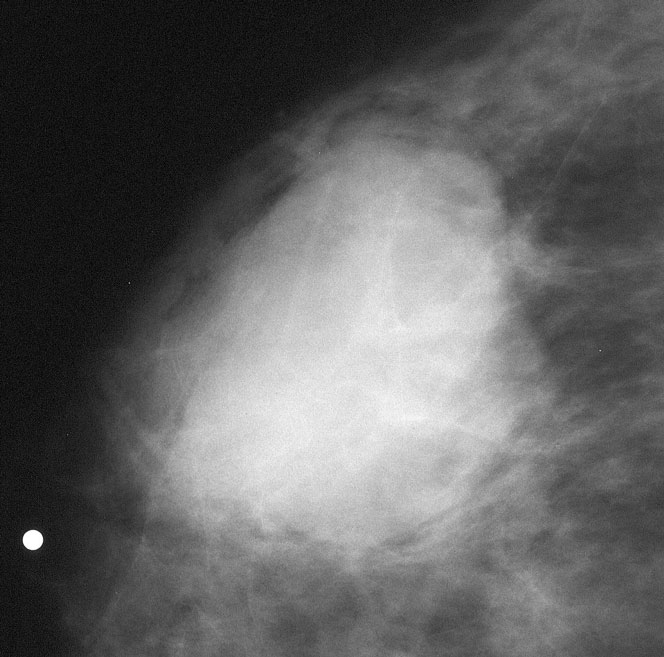
Do you think the margins are circumscribed?
YesNo
This mass is microlobulated inferiorly, and much of the margin is indistinct (poorly defined) and obscured (by overlying breast tissue). To be “circumscribed”, a mass must be well-defined (and not obscured) for at least 75% of its margin, and must lack more suspicious findings such as microlobulation and indistinct or spiculated margins.
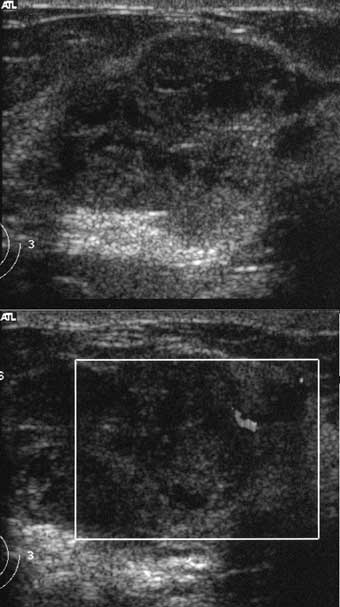
An ultrasound was performed.
What is your final assessment?
BI-RADS 2 - Benign - Appearance consistent with fibroadenomaBI-RADS 3 - Probably Benign - Likely a fibroadenoma
BI-RADS 4 - Suspicious - Possibly a fibroadenoma but warrants tissue diagnosis to rule out carcinoma
BI-RADS 5 - Highly Suggestive of Malignancy - Highly likely to be cancer
This mass has suspicious margins on spot mags and is solid and heterogeneous on ultrasound. It lacks an echogenic pseudocapsule, which is a sign of a fibroadenoma or other benign tumor according to Stavros (Radiology 1995). There is significant internal blood flow. These findings are suspicious, although it is possible that this is a fibroadenoma in this young woman.
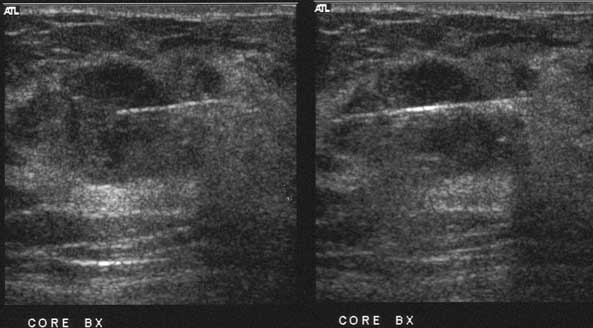
A core biopsy was recommended.
What images should you obtain at the time of the core biopsy?
Orthogonal images of the mass to be biopsiedPre-fire images with the needle in place
Post-fire images with the needle in place
Post-biopsy images of the mass
All of the above
Before performing core biopsy, one should always document images of the mass about to be biopsied, generally with at least two orthogonal views. This establishes images in your institution (often images done in the diagnostic work-up are performed at another location). It also documents that the mass being biopsied is indeed the mass recommended for biopsy. It also documents the appearance pre-biopsy, since it may change post-biopsy.
It is critical to obtain an image showing the needle in the mass. This documents that you have sampled the mass. I generally obtain a pre- and post-fire shot for each core sample. I obtain 3 good core samples so the pathologist has enough tissue to analyze.
It is not critical to obtain post-biopsy images, unless the appearance of the mass changes significantly OR a clip is placed and mammographic confirmation is desired OR there is a question as to whether or not the ultrasound mass is the same as the mammographic mass, this can be confirmed after the biopsy if the clip is placed.
The most likely pathology is
They tend to be round or oval solid masses because they make mucin. Tubular carcinomas present as small spiculated masses because they form spiculated tubules. This could be an adenoid cystic carcinoma, but these are rare compared with mucinous tumors. DCIS rarely presents as a well defined mass.
If Infiltrating ductal carcinoma, NOS had been offered as an answer, this would have been the best choice. Though IDC-NOS is usually spiculated, it can be well-defined. Since IDC-NOS is the most common type, it is the most likely cancer found when a well-defined mass is biopsied.
Mucinous carcinomaTubular carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma in situ
Adenoid cystic carcinoma