Teaching Files
Case 1
Contributed by: Steven J. Rockoff, MD and Diana L. Lam, MD - June 1, 2020
A 82-year-old woman presents for a screening mammogram:
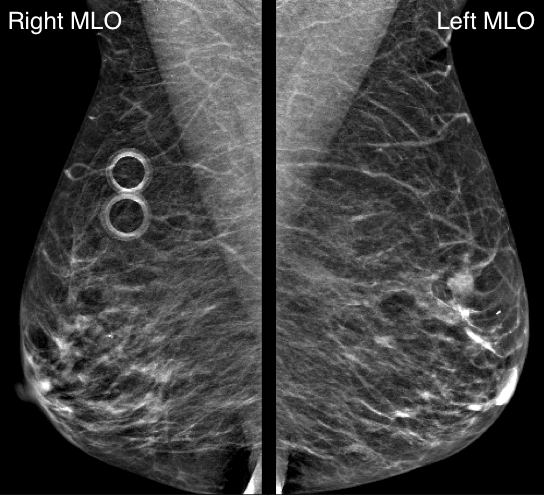
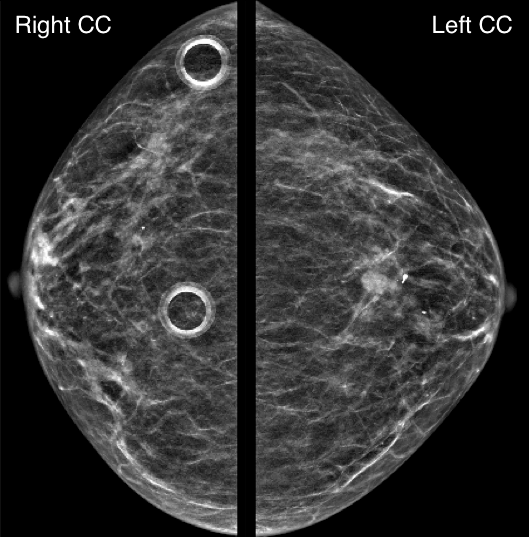
What is the dominant abnormality?
A. Mass in the right breastB. Mass in the left breast
C. Focal asymmetry in the right breast
D. Focal asymmetry in the left breast
E. No abnormality
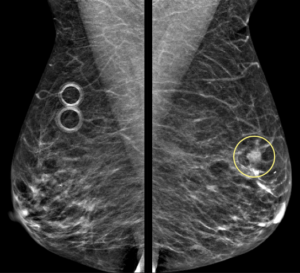
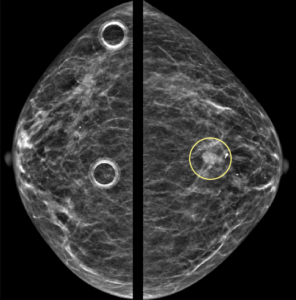
Explanation: According to the ACR BI-RADS Atlas, a mass is a three dimensional, space-occupying finding that is seen on two different mammographic projections. It has convex-outward borders and is usually dense in the center compared to its periphery.
What is your assessment and recommendation?
A. BI-RADS 4 (Suspicious); Ultrasound-guided biopsyB. BI-RADS 4 (Suspicious); Stereotactic biopsy
C. BI-RADS 0 (Incomplete); Diagnostic MRI
D. BI-RADS 0 (Incomplete); Diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound
Explanation: One must become familiar with the BI-RADS Assessment Categories and their corresponding management recommendations. The next step in the work-up of a screen-detected, potentially suspicious mass is diagnostic mammography and ultrasound. In this situation, BI-RADS Assessment Category 0 (“Need Additional Imaging Evaluation”) should be assigned and the patient is recalled for dedicated imaging of the finding.
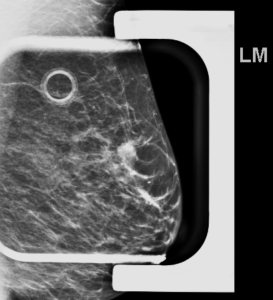
Left breast diagnostic mammogram performed with spot compression confirmed the presence of an irregular mass with obscured margins:
Targeted ultrasound at the 12:00 position revealed:
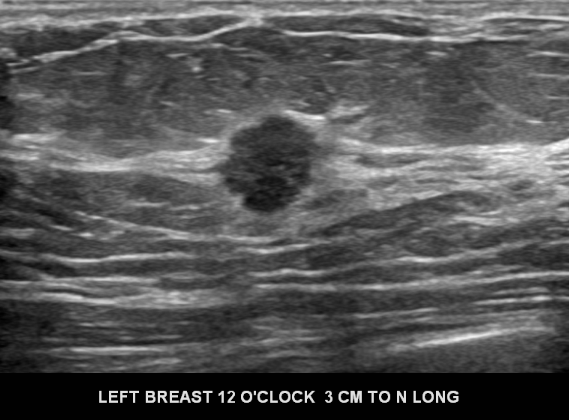
What is the best descriptor for the sonographic margins of this hypoechoic mass?
A. CircumscribedB. Angular
C. Microlobulated
D. Indistinct
E. Spiculated
Explanation: A mass’s margins can appear different between the mammographic and sonographic modalities. When assessing sonographic mass margins, the first step is to determine if this mass is circumscribed (sharply-defined around the entire circumference with an abrupt transition between the mass and surrounding normal tissue) or not circumscribed. “Not circumscribed” is further subdivided into:
- Angular
- Indistinct
- Microlobulated
- Spiculated
The ultrasound margins of this mass are best described as microlobulated, meaning that the dominant feature is multiple small undulations.
A helpful mnemonic to remember the non-circumscribed types of margins is “AIMS“.
What is your assessment and recommendation?
A. BI-RADS 3 (Probably Benign); Recommend six month follow-upB. BI-RADS 3 (Probably Benign); Recommend ultrasound-guided biopsy
C. BI-RADS 4 (Suspicious); Recommend six month follow-up
D. BI-RADS 4 (Suspicious); Recommend ultrasound-guided biopsy
Explanation: Diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound has confirmed the presence of a suspicious mass. BI-RADS Assessment Category 4 (“Suspicious”) is assigned and tissue sampling with biopsy is recommended in order to arrive at the final diagnosis. When technically feasible, ultrasound-guided biopsy is preferred over stereotactic biopsy due to the ability to see the target in real time while acquiring samples.
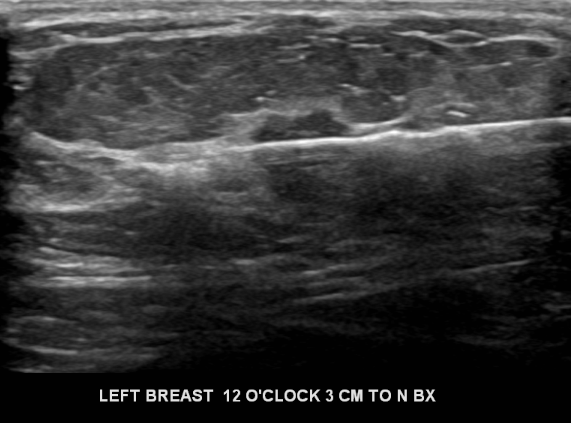
Ultrasound-guided biopsy revealed invasive ductal carcinoma.